Would like to obtain more info and learn more of its applications?
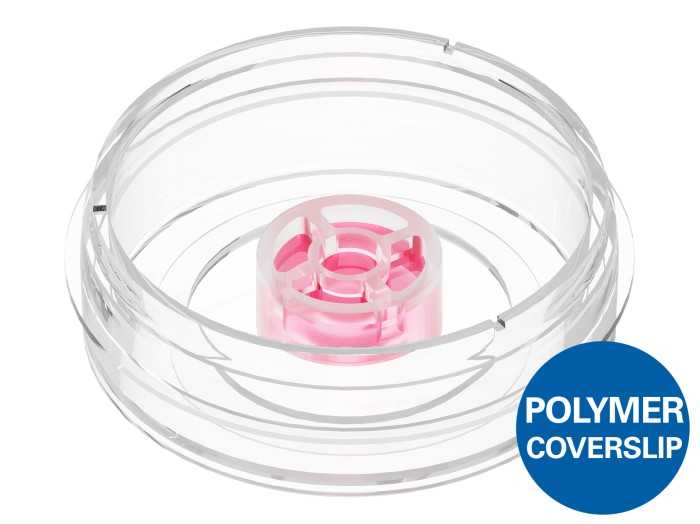
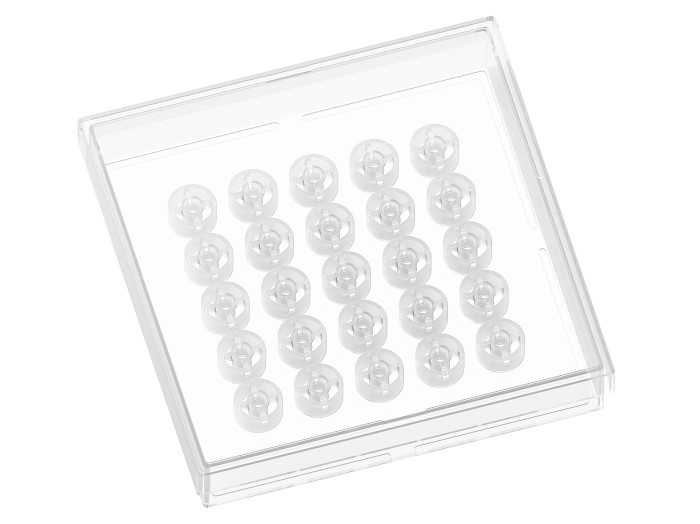
Micro-Insert 3D
A silicon insert designed for gel matrices and cellular interfaces, allowing a long-term, high resolution live cell imaging of cells inside or on top of a hydrogel matrix.


Barrier
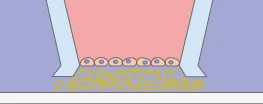
A cell monolayer is cultivated on a hydrogel matrix creating a cellular barrier
Migration
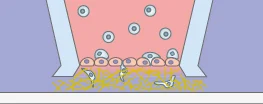
Transmigration of e.g. leukocytes through a cell monolayer
Tumor Angiogenesis
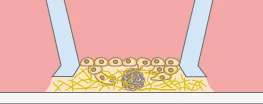
Sprouting of e.g. endothelial cells towards tumor cells
Air-Liquid Interphase
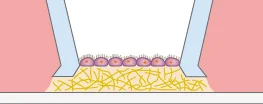
A monolayer of e.g. epithelial cells cultivated on a hydrogel matrix
Co-Culture
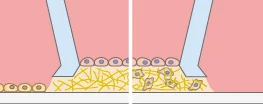
A cell monolayer cultivated on a hydrogel matrix while a second cell type is present either inside the 3D matrix or as a 2D monolayer
Advanced Co-Culture
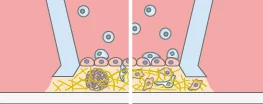
Transmigration of e.g. immune cells across a cell monolayer into a 3D gel matrix with embedded tumor cells
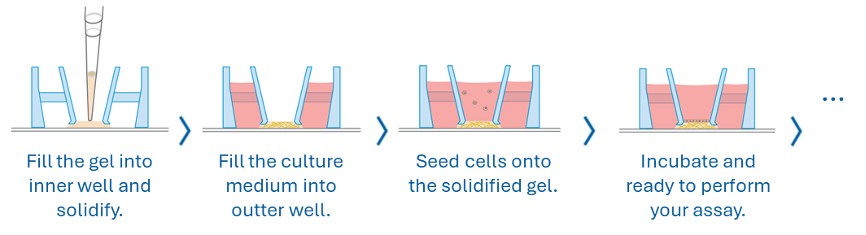

Movie: Handling the micro-Insert 3D
Advantages of micro-Insert 3D over transwell®
 |  | |
|---|---|---|
Cell Interface With a Membrane Insert | Cell Interface With the micro-Insert 3D | |
Principle | Cells on porous membrane | Cells on hydrogel matrix |
Preparation | Coating with protein of choice | Casting hydrogel of choice: e.g., ECM modelling |
Diffusion | Limited diffusion; dependent on pore size, membrane thickness and porosity | Open for diffusion; tunable by choice of gel matrix |
Mechanical properties | Stiff polymer membrane – artificial | Soft gel matrix; physiological |
Chemical properties | Membrane is inert; no biological interaction | Hydrogel can be remodeled – cell interaction possible |
Cell retrieval | Mechanical scraping, chemical trypsinization | Gel digestion, mechanical retrieval |
Microscopy access | Poor: membrane cutting necessary | Good: direct microscopy access |
Imaging quality | Poor: image quality is affected by the membrane | Good: image quality is defined by the gel matrix |
A silicon insert designed for gel matrices and cellular interfaces, allowing a long-term, high resolution live cell imaging of cells inside or on top of a hydrogel matrix.


Barrier

A cell monolayer is cultivated on a hydrogel matrix creating a cellular barrier
Migration

Transmigration of e.g. leukocytes through a cell monolayer
Tumor Angiogenesis

Sprouting of e.g. endothelial cells towards tumor cells
Air-Liquid Interphase

A monolayer of e.g. epithelial cells cultivated on a hydrogel matrix
Co-Culture

A cell monolayer cultivated on a hydrogel matrix while a second cell type is present either inside the 3D matrix or as a 2D monolayer
Advanced Co-Culture

Transmigration of e.g. immune cells across a cell monolayer into a 3D gel matrix with embedded tumor cells


Movie: Handling the micro-Insert 3D
Advantages of micro-Insert 3D over transwell®
 |  | |
|---|---|---|
Cell Interface With a Membrane Insert | Cell Interface With the micro-Insert 3D | |
Principle | Cells on porous membrane | Cells on hydrogel matrix |
Preparation | Coating with protein of choice | Casting hydrogel of choice: e.g., ECM modelling |
Diffusion | Limited diffusion; dependent on pore size, membrane thickness and porosity | Open for diffusion; tunable by choice of gel matrix |
Mechanical properties | Stiff polymer membrane – artificial | Soft gel matrix; physiological |
Chemical properties | Membrane is inert; no biological interaction | Hydrogel can be remodeled – cell interaction possible |
Cell retrieval | Mechanical scraping, chemical trypsinization | Gel digestion, mechanical retrieval |
Microscopy access | Poor: membrane cutting necessary | Good: direct microscopy access |
Imaging quality | Poor: image quality is affected by the membrane | Good: image quality is defined by the gel matrix |
Would like to obtain more info and learn more of its applications?
